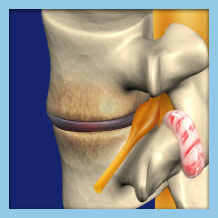
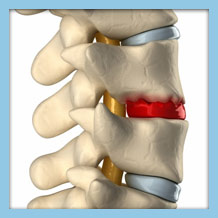
How Do I Know if I Have Degenerative Disc Disease?
Symptoms of degenerative disc disease usually include mild pain in the area affected that worsens as more pressure is placed on it. Numbness, tingling, and radiating pain are often felt in the arms or legs, depending on where the disc degeneration is occurring. When the degeneration is in the neck symptoms will be felt in the shoulders and arms. If the degenerated disc is in the lower back, symptoms will be felt in the legs. Symptoms of degenerative disc disease will worsen as the condition progresses if not treated.
Do you have any of these symptoms and think you may be suffering from degenerative disc disease? We have a quick and easy tool to help gather some information from you to help us determine what your problem is and get you on the road to recovery.
What Degenerative Disc Treatment is Right for Me?
Early degenerative disc treatment includes anti-inflammatory medications, the application of heat and ice, and exercise to strengthen back muscles that provide support to the spinal structure. Further conservative treatment usually requires the patient to undergo physical therapy. Only once conservative treatments have been exhausted should surgery be considered.
OLSS provides numerous degenerative disc treatment options and doctors who are experienced in the most advanced treatments.
The real question is: What treatment is best to treat your degenerative disc disease? Use our Treatment Match tool to quickly get started in finding the right treatment for you.
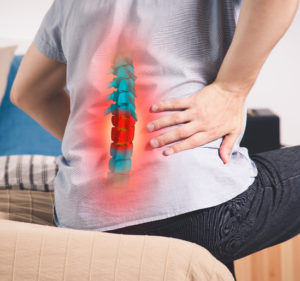
Best Treatment to Prevent Pain From Degenerative Disc Disease
If you are experiencing any symptoms of degenerative disc disease, there are various treatments you can do for pain relief. If you are not experiencing serious pain, then you should try some home treatments first. However, this will depend on the level of pain a person is dealing with. Below will be a list of non-surgical and surgical procedures to follow for the proper treatment:
Non-surgical treatments:
- Home treatments- use ice or a heating pad on the area of pain. Take medication such as ibuprofen or naproxen for inflammation.
- Physical therapy/ Exercise- getting guidance from a physical therapist will help the patient get the appropriate care. Exercising can help strengthen and stretch the back.
- Lifestyle adjustments- limiting activities that increase pain, getting into bed rest for a few days, and doing light exercises such as walking and swimming.
Surgical treatments:
- Spinal Laminectomy– limiting pressure on the spinal cord. Trimming a part of the spinal ring that covers the lamina which is also the spinal cord. This helps widen the spinal canal which usually creates more space for the spinal nerve.
- Facetectomy– a procedure that removes a part of the facet joint. This develops space and relieves pressure on the spinal nerve root.
- Laminoplasty– a procedure that repairs a cervical neck spine to create room for the spinal cord.
